If routing can be compared to the post-mailing system, then Deep Packet Inspection “DPI” should be equal to the Airport Security. Today we're going to take a dive into the Best Deep Packet Inspection Software and Tools of 2024 and jump into a short tutorial and Guide.
Just like a postman that looks at the package recipient label— the job of a networking device (or router) is only to look at the header of the IP packet, look at the destination address, make a decision, and route as fast as possible.
Here is our list of the top packet analysis tools:
- ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer – FREE TRIAL This package provides a range of methods to examine and record packet details including flow protocols and DPI. Runs on Windows Server, Linux, and AWS. Download the 30-day free trial.
- Paessler Packet Sniffing with PRTG This module doesn’t collect packets but generates statistics from their headers, Available as a SaaS package or for installation on Windows Server.
- ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer This package provides a range of methods to examine and record packet details including flow protocols and DPI. Runs on Windows Server, Linux, and AWS.
- nDPI with ntopng This package is based on OpenDPI and it will analyze packets that are being processed by ntopng. Available for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Netifyd This adaptation of nDPI is designed as a collector that you can use to feed packet header data into analytical systems. Available for Linux, BRD, and network device OSs.
Looking at just one portion of the packet makes routing much more efficient and fast. But in the post-mailing system, a mail carrier cannot open the package to inspect its contents.
You can leave this to the Transportation Security Airport “TSA.” They are the ones with the technology, resources, and permission to check every single passenger, bag, and package.
In the networking space, a router can do a lot more than just checking the destination address. With the DPI technology, a router can look deep into the contents of the package and make decisions accordingly.
What is DPI and How it Works?
Deep Packet Inspection “DPI” is a sophisticated method to examine the contents of network traffic. It can filter packets based on in-depth analysis at all layers of the OSI model.
As mentioned before, a router would typically only look at the IP header of a packet. In the case of a stateless firewall (also known as an ACL “Access Control List”), it would only check connections based on source and destination IP addresses.
To help clarify this, use the picture below. An L3 router or stateless firewall would only work in the Network layer and below.
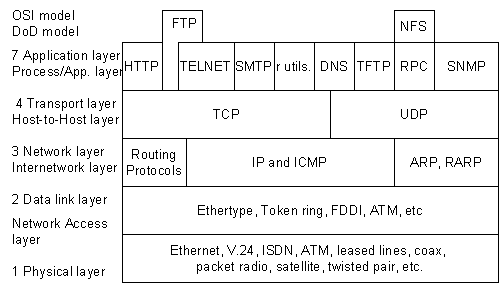
But routing and firewalling methods are evolving over the years. The firewall technology had to evolve and adapt the “shallow packet inspection technology” to protect the network from the increasing variation of attacks.
In the same case, to route based on the transport layer, the L4 switch was born. The stateful firewall would watch the traffic from end to end, by digging “shallowly” into the TCP/UDP connection.
In other words, a stateful firewall performs a superficial inspection to the transport layer and can identify the using ports whether is HTTP, SMTP, SNMP, DNS, etc.
Reverse Engineering DPI
To understand shallow/deep inspection, you need to know how a network package is encapsulated. Refer to the picture below. An application, such as DropBox, Skype, or BitTorrent creates data.
This data is encapsulated in the Transport layer into a TCP segment with a UDP/TCP header. The segment is then encapsulated into an IP datagram on the Internet layer, with an IP header. Finally, it is turned into a datagram in the layer 2 with a frame header and sent over to the physical media.
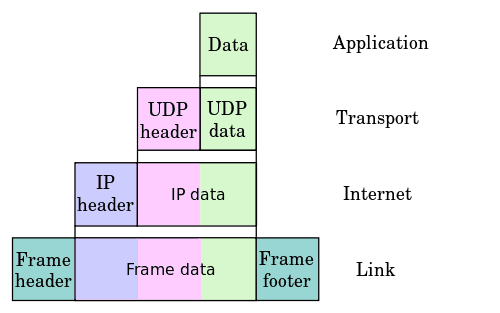
A stateful firewall can find out which application protocol was used by looking into the TCP segment of the transport layer, but it is not able to see the data itself.
DPI technology takes a step forward.
It can open the packet and look through Layer 2-7 of the OSI model. In other words, the DPI technology can look into:
- Layer 2 frames.
- Layer 3 IP headers.
- Data protocol structures
- But most importantly, the Payload of the message
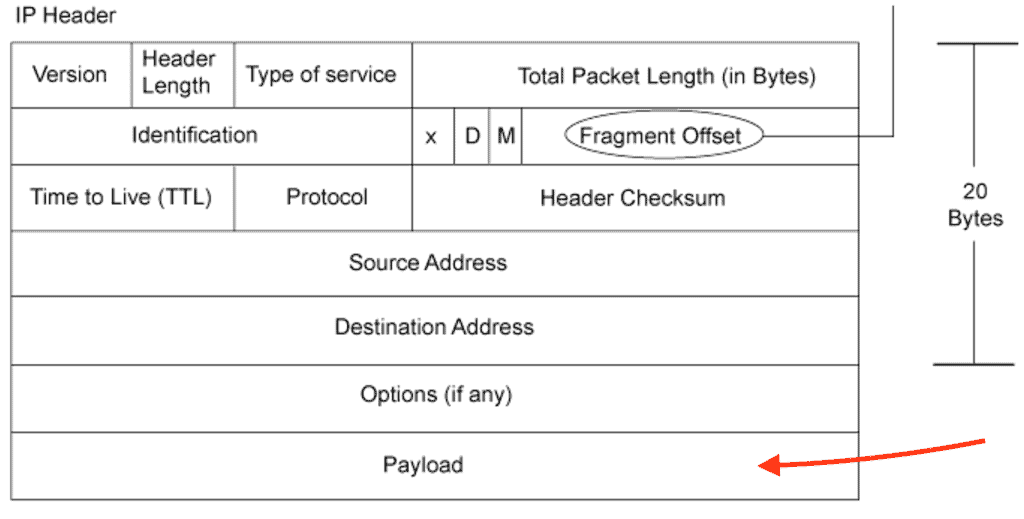
The payload is the actual data that is not supposed to be discarded or opened until it reaches the final destination. If you capture traffic flow and open a single packet from the specific source/destination in Wireshark, you could open it and view its payload (just like DPI would).
The problem here is that the results are too verbose. To make some sense out of this, you might need to do a lot of conversions on Hexadecimal to Decimal; it would be too time-consuming for only one packet.
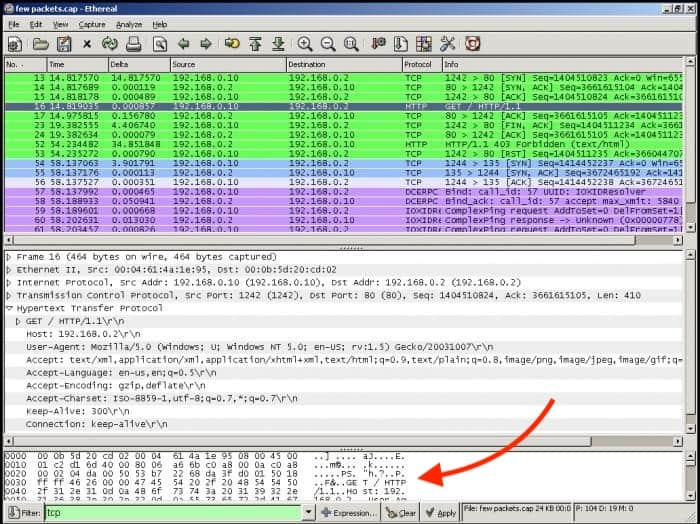
A DPI-enabled router or firewall has access to all information in the payload and uses libraries to make sense out of this data. A device with DPI can be configured with policies and can make decisions based on layer 7 data, and block, re-route or keep logs of the traffic.
What's The Importance of DPI?
DPI is so important because it can help large corporations improve their security standpoint by shaping its traffic. But not every router (or firewall) can handle deep packet inspection. The technology requires substantial resources to work, so it is not common in SMBs (Small-to-Medium-Businesses), and if not configured correctly, it can be a real traffic bottleneck.
A router with DPI needs to be powerful to be able to open every packet, inspect it, wrap it, and send it again. Only large enterprises, governments, and telecom service providers have the resources to put this technology to work.
DPI can is used in a Wide Variety of Applications.
It can help a corporation guarantee that the data sent and received does not contain malicious code and detect advanced cyber-attacks. On the other hand, DPI can also be used for other motives, such as eavesdropping, re-directing, or block specific traffic.
An example of DPI in action is when an ISP wants to shape the traffic. If there is traffic that is too demanding on their networks, such as streaming media or torrents, they might want to open such packets and shape the traffic accordingly.
ISPs might also use it to drop packets coming from specific websites, such as competitors, adult content, piracy, etc.
IPS/IDS Systems Using DPI Analysis.
An Intrusion Detection System “IDS” is capable of detecting intrusions, but it cannot block an attack.
An IDS can employ Deep Packet Intrusion technology to help it:
- Collect more information on the attack.
- Identify some attack signatures and patterns.
- Controls network traffic such as FTP root access, Telnet, or specific HTTP content.
IDS that rely on DPI can inspect the content of packets and get more information. With this technology, an IDS can identify an attack faster and even control it. The IDS compares the attack to a database to match it against attacks signatures and lets DPI act according to its policies.
On the other hand, an Intrusion Detection Systems “IPS” can detect and block attacks in real-time. Some “IPS” solutions also implement DPI technologies to help prevent attacks. It can:
- Prevent certain attacks signatures.
- Protect against certain vulnerabilities and exploits.
In most cases, a DPI can improve the security standpoint of conventional solutions.
DPI incorporates the capabilities of IDS/IPS with a traditional stateful firewall, making it capable of finding attack variations that these devices cannot identify by themselves.
Here's the Best Software for Deep Packet Inspection of 2024:
DPI usually comes as a feature in security appliances or as a virtual DPI deployed in a server.
Although a proper implementation is to employ a dedicated security/DPI appliance, you might also want to implement DPI as a service or through software.
Below you'll find a quick description of each product as well as some screenshots and where to download them to test them out!
Our methodology for selecting Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) tool:
We've broken down our analysis for you based on these key criteria:
- Capability to analyze network traffic in-depth.
- Support for multiple protocols and analysis methods.
- User interface and ease of use.
- Pricing and availability of a free trial or free version.
- Ability to integrate with other network monitoring tools.
1. ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer – FREE TRIAL
ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer gets its name from the NetFlow protocol, which is a network device activity recording system that was invented by Cisco. This tool can get that data out of devices. The package also provides the Network Packet Sensor, which gives you the option to read packet headers and collate statistics.
Key Features:
- NetFlow, sFlow, J-Flow, IPFIX, AppFlow, and Netstream
- Protocol analysis
- Multiple analysis methods
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer stands out for its ability to support various flow protocols, coupled with efficient data management, making it ideal for in-depth network analysis.
The DPI feature of the Network Packet Sensor is also able to read the data payload of packets. However, much of your traffic will contain encrypted data, so don’t expect to be able to read those contents. You will certainly be able to see header data, which gives you protocol analysis.
This system doesn’t store packets like Wireshark, so it doesn’t build up massive files on your disks. This is an efficient analysis method because you get all of the essential information without vast amount of data storage. The package will show time-series graphs and analyze traffic by protocol/application, source, and destination.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is highly recommended for network administrators and IT professionals who require detailed traffic analysis without the data storage burden, especially in environments where multiple protocols are in use.
Pros:
- A choice of flow protocols or DPI for traffic sourcing traffic statistics
- Time-series live activity graphs
- Historical analysis
Cons:
- No SaaS option
There are four editions for ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer and here are their base prices:
- Free: $0 – restricted to monitoring two interfaces
- Standard: $8,595 – for 500 interfaces
- Professional: $595 – 10 interfaces
- Enterprise: $1,045 – 10 interfaces
You can get a 30-day free trial from this package that runs on Windows Server and Linux. You also get the free trial with the version that is available on AWS Marketplace.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer is our top network monitor because it offers a comprehensive set of features suitable for detailed network traffic analysis. It supports various flow protocols and integrates DPI for in-depth traffic sourcing, making it versatile for different network environments.
The tool is efficient in data handling, providing essential information without requiring large storage space. It's especially beneficial for those seeking detailed traffic analysis without the complexity of storing massive data files. Plus, its free trial on Windows Server and Linux makes it accessible for a broad range of users.
Download: Start a 30-day FREE Trial of ManageEngine NetFlow Analyzer
OS: Windows Server, Linux
2. Paessler Packet Sniffing with PRTG
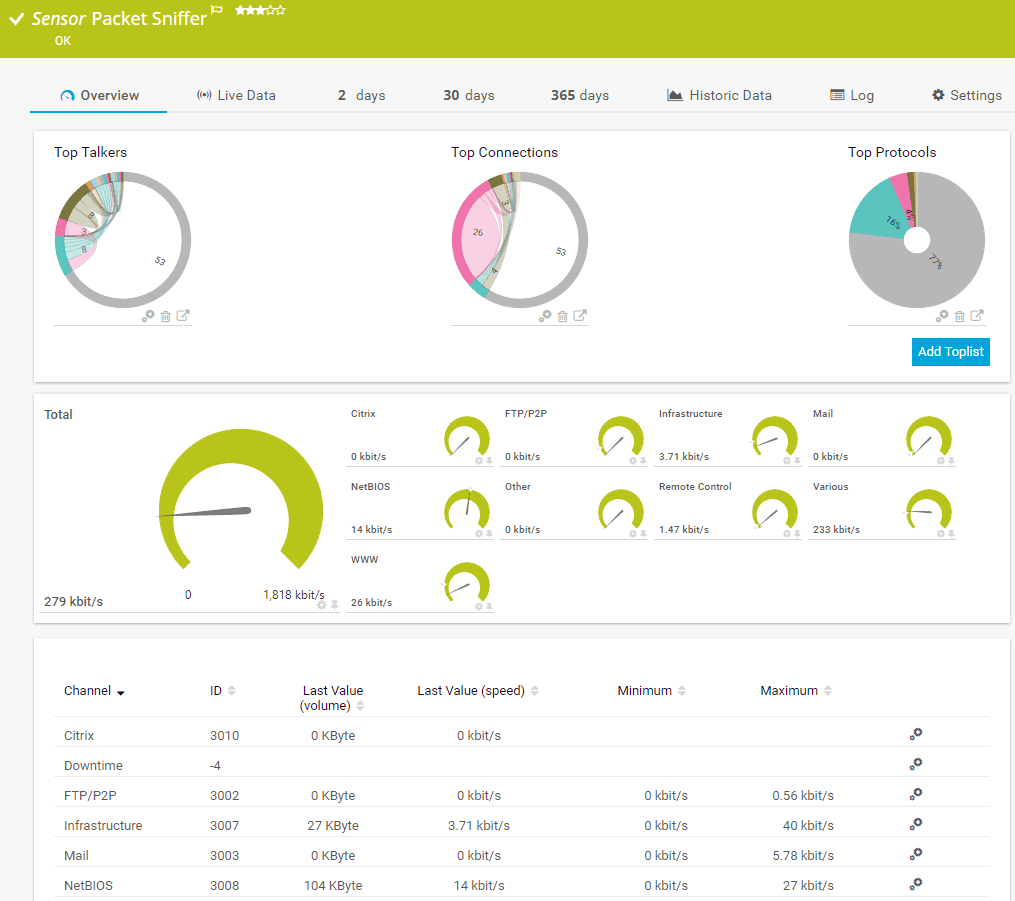
A packet sniffer analyzes network traffic similar to DPI. PRTG employs a packet sniffer sensor to capture every packet that is transmitted on the network and digs deep into its content.
Key Features:
- Packet header statistics.
- Diverse technology integration.
- Free version available.
- On-premises or SaaS options.
Why do we recommend it?
PRTG's strength lies in its multi-technology approach, combining packet sniffing with SNMP and WMI for comprehensive network performance reporting.
To achieve this, PRTG uses different technology, such as SNMP, Netflow, WMI, REST APIs, and packet sniffing. Network admins use PRTG mainly for troubleshooting network problems or collecting detailed statistics. Just like DPI, it can also help identify bandwidth consumption trends, for example, a File Sync or Cloud App that is consuming too much bandwidth.
PRTG’s packet sniffer can also help improve the security standpoint, by identifying different types of traffic, such as P2P or possible attacks.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for network admins seeking a versatile tool for troubleshooting, security enhancement, and bandwidth consumption analysis, PRTG's diverse technology integration makes it a robust choice.
Pros:
- Uses a combination of packet sniffing, WMI, and SNMP to report network performance as well as discover new devices
- Autodiscovery reflects the latest inventory changes almost instantaneously
- Drag and drop editor makes it easy to build custom views and reports
- Supports a wide range of alert mediums such as SMS, email, and third-party integration
- Supports a freeware version
Cons:
- Is a very comprehensive platform with many features and moving parts that require time to learn
With PRTG you can choose a license based on sensors. To give you an idea of the pricing and their predefined packages of sensors: PRTG500 (500 sensors for $1365.00), PRTG2500 ( 2500 sensors for $5100), PRTG XL1 (Unlimited sensors for $11,500). An unlimited version of PRTG for 30 days.
3. nDPI with NTopng
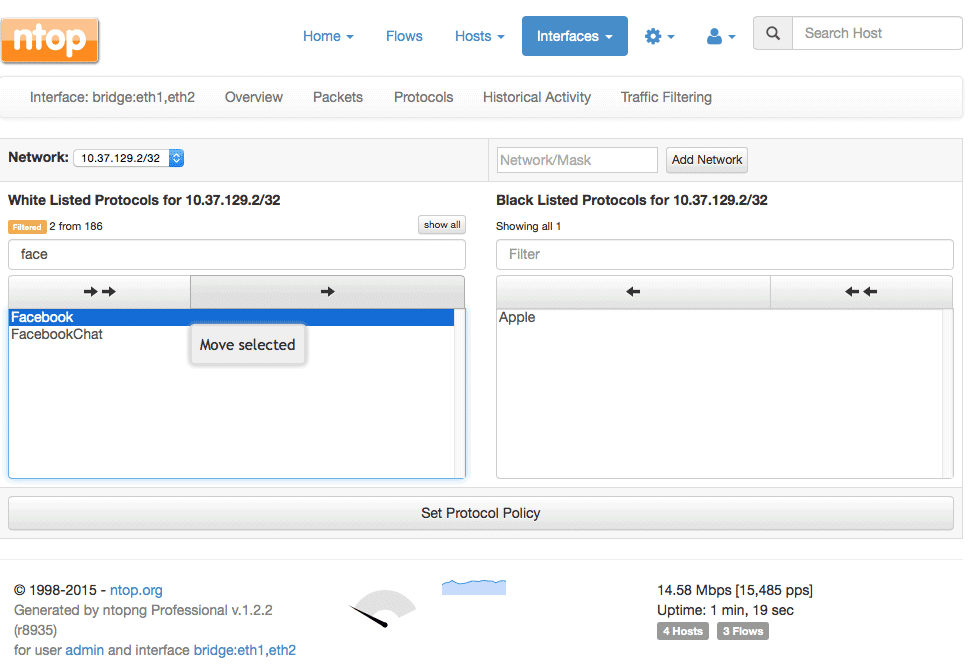
NTop is a network monitoring suite. It has a variety of products for Packet Capture, Traffic Recording, Network Probe, Traffic Analysis, and DPI. DPI from NTop is performed by nDPI with the help of NTopng. nDPI is an open source and extensible DPI library, based on the popular OpenDPI.
Key Features:
- NTopng integration.
- Open-source and free.
- Based on OpenDPI.
Why do we recommend it?
nDPI with NTopng is recommended for its open-source nature and integration with NTopng, providing a cost-effective solution for traffic analysis and policy application.
A network admin can use this tool to block specific traffic flows, hosts, or network protocols. But since nDPI is only a library, it must be used with other apps such as ntopng and nProbe cento to perform the rules.
NTopng is the web interface monitoring tool that can passively collect traffic from a network interface to show status and performance. With ntopng and ndpi you can apply L7 policies, such as shaping the traffic of specific applications within a network subnet.
Who is it recommended for?
Network administrators who prefer open-source solutions and need a tool to apply Layer 7 policies effectively will find nDPI with NTopng particularly useful.
Pros:
- Open-source project with full transparency
- Free version available alongside the enterprise version
- Special licensing options for nonprofits and educational institutions
Cons:
- User interface is easy to use, but could be improved upon
It is a free and open source software. Find the source code, here.
5. Netifyd
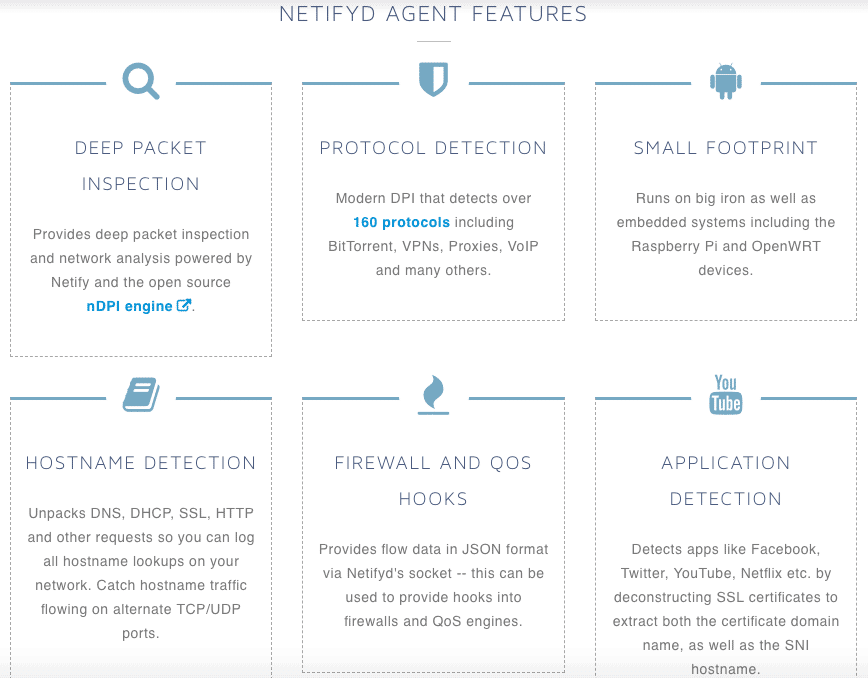
The Netify Agent or Netifyd is a DPI engine based on the open source nDPI. The software is capable of categorizing traffic patterns and identifying protocols such as Skype, P2P, Plex Media Server, etc.
Key Features:
- Open-source nDPI based.
- Free with paid options.
- Effective metadata extraction.
Why do we recommend it?
Netifyd is recommended for its ability to categorize traffic patterns efficiently and its flexibility in offering both free and paid extensions.
Netifyd empowers from the DPI technology to open packets on the application layer, look at HTTPS certificates and detect websites/apps such as Youtube, Facebook, Netflix, etc. Netifyd captures traffic passively which means that it does not blocks, filters, or manipulates traffic.
Netifyd just provides DPI services to other tools. These traffic packets are then scanned through the nDPI protocol to detect packet flows.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is suitable for network administrators in smaller network deployments who need a minimalistic, yet effective DPI solution.
Pros:
- Transparent open-source project
- The dashboard is minimalistic and good for smaller network deployments
- Paid version if affordable, even for smaller labs
Cons:
- Another fork of OpenDPI can be a con if you’re not a fan of that framework
- No packet analysis functionality
- Only supports application layer scanning
The pricing of Netify is based on three models, Basic ($50 /per agent per month), Pro ($100 /per agent per month), and Flex (contact them). Get the 15 day trial of Netify for free.
Conclusion, What’s Next?
DPI can help improve a network security standpoint, by enhancing the functionalities of firewalls, IDS, and IPS. It can also shape the traffic to solve problems faster and improve bandwidth consumption.
Some DPI solutions can also develop the limitations of IDS/IPS. Some of these services that rely on DPI offer additional functionalities such as, malware analysis, anti-spam filtering, buffer overflow, DoS attack prevention, VPNs, URL filtering, etc.
But DIP is a high resource consumption technology, so it is reserved for large enterprises, ISPs, and even governments. It has always been state-of-the-art network management and now it is used in different scenarios other than security and routing.
It is helping companies with Internet data mining, block traffic to competition, eavesdropping, and even Internet censorship. If you have a powerful server or want to test the DPI functionality on a small scale, download one of the tools shown above and give them a try!
Deep Packet Inspection FAQs
What is deep packet inspection?
Deep packet inspection (DPI) is a technology used to examine the contents of network traffic at a granular level. It allows for the analysis of individual packets of data, enabling the detection of specific protocols, applications, and content.
How does deep packet inspection work?
Deep packet inspection works by intercepting and analyzing network traffic in real-time. It looks beyond the basic header information of network packets to examine the payload contents. This enables the identification of specific protocols, applications, and content.
What are some common applications of deep packet inspection?
Common applications of deep packet inspection include network security, traffic analysis and optimization, and compliance monitoring. It is also used in network forensics, intrusion detection, and content filtering.
What are some benefits of deep packet inspection?
Some benefits of deep packet inspection include improved network security and threat detection, enhanced network performance and optimization, and better compliance monitoring and reporting. It can also help identify network issues and inefficiencies, enabling proactive network management and troubleshooting.
What are some potential risks or drawbacks of deep packet inspection?
One potential risk of deep packet inspection is the potential for invasion of privacy. The technology enables the examination of individual packets of data, which can include sensitive information such as personal data, login credentials, or confidential business information. There are also concerns around the potential misuse of deep packet inspection for surveillance or other nefarious purposes.
How is deep packet inspection different from other network monitoring technologies?
Deep packet inspection is different from other network monitoring technologies, such as network flow analysis or packet capture, because it provides more detailed information on the contents of network traffic. It enables the identification of specific protocols, applications, and content, enabling more granular analysis of network behavior and performance. This can be especially useful in identifying and mitigating security threats and optimizing network performance.