Today we're going to take a deep dive and review some of the Best Patch Management Tools & Software for your network infrastructure!
Keeping your systems up to date with patching and software updates is really important for your business.
Here is our list of the best patch management tools:
- Atera – EDITOR'S CHOICE This SaaS platform provides tools for remote monitoring and management that are packaged for use by IT departments and managed service providers. The platform includes an automated patching system for Windows, macOS, and Linux, plus third-party software. Start a free trial.
- Syncro – FREE TRIAL A cloud-based SaaS package that includes an automated patch manager for Windows and software as part of a remote monitoring and management (RMM) bundle. Start a 14-day free trial.
- SolarWinds Patch Manager – FREE TRIAL This process automation tool takes a lot of work out of managing patch rollouts by listing all of your OS and software versions and then checking for any updates. The tool will coordinate all of your endpoints and server to ensure that they are all up to the same version. Runs on Windows Server. Start a 30-day free trial.
- NinjaOne Patch Management – FREE TRIAL Formerly NinjaRMM, a remote monitoring and management system for managed service providers that include a patch automation service. This is a cloud platform. Start a 14-day free trial.
- SuperOps Patch Management – FREE TRIAL A cloud-based system that offers a full suite of RMM tools as well as a PSA module. Ideal for an MSP, an independent support technician, or an IT department.
- N-able N-sight Patch Manager – FREE TRIAL A cloud-based patch management service that is part of a remote monitoring and management platform.
- ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus – FREE TRIAL This service is able to manage patch statuses and roll-outs for devices that run Windows, Windows Server, macOS, and Linux. Installs on Windows Server and Linux.
- SecPod SanerNow Patch Management – FREE TRIAL A SaaS cyber-hygiene platform that offers automated patch management as part of a set of system security and management tools.
- Heimdal Security – FREE TRIAL simplifies Windows patch management through powerful automation, intuitive design, and object-based policies.
- Microsoft SCCM Patch Management A patch utility from Microsoft that keeps all Microsoft products up to date including Windows and Windows Server.
- Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Manager A vulnerability scanner and patch automation system for Windows, macOS, and Linux that also updates software packages.
- Kaseya VSA Patch Management Patches Windows, macOS, and third-party software. This is part of Kaseya VSA, which is aimed at managed service providers.
- GFI LanGuard This patch automation system runs on Windows and patches Windows, Windows Server, Linux, and macOS over a network.
- ITarian Patch Management ITarian was previously known as Comodo One. It is a remote monitoring and management platform that includes patch management for Windows, Linux, and third-party software.
- Symantec Patch Management Solution Symantec offers a range of patch management solutions that are marketed per operating system and are available for endpoints and servers.
Malware and viruses are capable of compromising your data and network through poorly maintained software updates, especially in light of recent developments such as ransomware.
Less obvious threats come in the form of exploits, which allow hackers to enter into your network without being detected.
Data leakage and exfiltration occur in this scenario, opening you and your business up to liabilities and privacy breaches, meaning that your customers could take you to court over leaked information, especially if it is private and confidential.
The past few years have seen massive data breaches affecting big companies such as Google’s Google Plus and Uber.
These are companies that have seemingly unlimited IT budgets, yet they manage to fall prey to crafty hackers, poorly implemented patching, and Malware. If it can happen to big companies, then it can happen to you.

All of this sounds scary, and in a lot of ways it is, but what better way to protect yourself and your business interests is there than to keep your IT infrastructure patched and up to date?
With this in mind, we will take a look at the current state of patching software that is available on the market, and hopefully allow us to show you which patch management applications would work best for you. Let’s get started with our selected products.
The best way to combat cybercriminals is to make sure that your IT infrastructure follows best practice standards, of which patching is one of great importance.
Instead of worrying about your IT infrastructure and manually patching all of your workstations, servers, and appliances, why take a look at some of the products in our patch management roundup.
The Best Patch Management Tools & Software
What should you look for in a patch management tool for Windows?
We reviewed the market for patch management software that runs on Windows and analyzed options based on the following criteria:
- Autodiscovery of all devices connected to a network
- Endpoint scanning to compile a software inventory
- Regular polling for patch availability
- Integration with WSUS and SCCM or adaptation of those systems
- Logging of patching actions for compliance reporting
- A system that is provided through a free trial to enable a no-risk assessment
- A comprehensive patch manager that provides value for money by being made available at a fair price
With these selection criteria in mind, we identified a shortlist of patch management systems that implement automated updates and we have includes systems that are delivered as SaaS platforms as well as on-premises software packages.
Below you'll find a List of Software from above, along with a quick description of each one – After you have looked at all of these options, you can decide which one could work best for you in your environment.
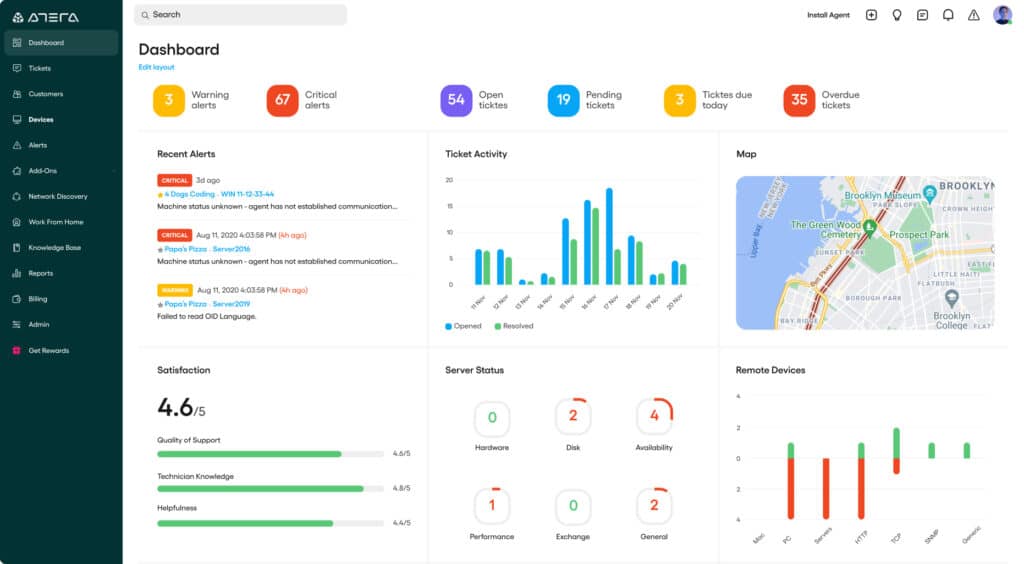
1. Atera Patch Management – FREE TRIAL
Atera Patch Management is a module of a remote monitoring and management (RMM) platform. The RMM in turn is offered in a bundle with a professional services automation (PSA) system. These two services together give managed service providers (MSPs) all of the software that they need in order to operate.
Key Features:
- Part of an RMM
- Multi-tenant option
- Operates on Windows and macOS
Why do we recommend it?
Atera Patch Management is highly efficient and tailored for MSPs and IT departments, offering comprehensive patch management, along with a suite of monitoring and management services.
The Atera system is able to patch Windows and Windows Server, Microsoft Office, hardware drivers, Adobe products, and Java. You can also set up automated software patch management for MacOS and Windows via Homebrew and Chocolatey integrations. The list of patches includes Chrome, Zoom, Skype & Dropbox among others.
The patch management system gathers available patches and allows the technician to schedule installation to run out of office hours. Individual patches can be excluded from a roll-out, either permanently or temporarily. Patches can also be applied individually on a schedule or on-demand.
The Atera system is a cloud-based platform, so it does not need to be downloaded. However, each client system being monitored will need an agent program installed on it. The Atera functions can be applied to several systems per account. The system isn’t charged per monitored system, so there is no software overhead incurred by taking on a new client. Instead, Atera charges a subscription per month per technician. The service is available in three editions: Pro, Growth, and Power – all of these include the Patch Management module.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for MSPs and IT departments that need an integrated solution for endpoint management, patching, and professional services automation.
Pros:
- Minimalistic interface makes it easy to view the metrics that matter most
- Flexible pricing model makes it a viable option for small businesses
- Includes multiple PSA features, great for helpdesk teams and growing MSPs
- Can track SLAs and includes a time tracking option for maintenance tasks
Cons:
- Focuses heavily on MSP related tools, other businesses may not be able to utilize multi-tenant features
Prices are per technican per month: Pro = $129, Growth = $179, Power = $209. Atera is a cloud-based platform, so there are no downloads needed in order to use it. The service can be experienced on a free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
Atera is our top pick for a patch management tool because this cloud platform provides tailored service packages for managed service providers and IT departments that include patch management along with many other system monitoring and management services. The Atera platform is able to manage endpoints running Windows, macOS, and Linux with a patch manager that integrates scheduling for software updates and standard maintenance functions. You can write your own scripts for execution on remote endpoints and set them up in the Atera patch manager for scheduled and regular execution. Packages include many more features, such as automated monitoring and a Help Desk ticketing system
Download: Start a FREE Trial
Official Site: https://www.atera.com/signup/
OS: Cloud-based
2. Syncro – FREE TRIAL
Syncro is a cloud-based SaaS platform that provides tools for managed service providers. The remote monitoring and management (RMM) service of the platform is a toolkit for MSP technicians and it includes an automated patch manager. While the RMM package operates on remote endpoints running Windows and macOS, the patch manager will only update computers running Windows.
Key Features:
- An MSP tool
- Documents all software
- Patching for Windows and software
Why do we recommend it?
Syncro stands out for its comprehensive RMM package, including an automated Windows patch manager, offering efficient unattended patch rollout and detailed completion statuses.
The Syncro system is multi-tenanted, so the team manager can set up a subaccount for each client. The onboarding process for a client involves the installation of a local agent. This program scans each endpoint and installs a copy of itself. The endpoint agent sends details of the operating system and all of the software installed on the computer that hosts it.
The details that the Syncro system holds in its software inventory include the version number of each piece of software and the operating system. In the case of Windows PCs, the inventory forms the basis if an automated patching system. The version number reflects the patch status of the software and the Syncro system polls the provider frequently to check for new patches.
The system administrator of the MSP needs to set up a maintenance schedule for each client. This usually creates a weekly time window, which is probably out of office hours. The patch manager will queue up patches and run them automatically, unattended, at the next available maintenance window.
The patching system provides options for which patches to run, which to hold, and which to reject, based on the patch severity. Patching usually occurs out of office hours and the system will wake up all endpoints, install relevant patches, reboot where necessary, and then turn the endpoint off. Not all patches will complete successfully and the patch manager console shows the completion status of each patch for each endpoint with a reason for any failed patch.
Who is it recommended for?
Best for MSPs and IT teams that require a complete RMM solution with a strong focus on automated Windows patch management.
Pros:
- A complete RMM package that includes an automated patch manager
- Unattended patch rollout with completion statuses
- A library of task automation scripts for system maintenance
- A PSA package of services for use by the management of the MSP
Cons:
- Doesn’t patch computers running macOS
The subscription rate for Syncro is levied per technician at a price of $129 per month when paid annually or $139 when paid month to month. You can assess Syncro with a 14-day free trial.
3. SolarWinds Patch Manager – FREE TRIAL
SolarWinds Patch Manager is a simplified patch management solution that automates the patching and reporting process for you. This helps to save time and makes things a lot easier to run day to day from an administrative point of view. This will help you to keep your servers and workstations up to date and protected from the latest threats.
Key Features:
- Adapts WSUS
- Microsoft updates
- Third-party patches
- Operates on Windows
- Central management
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Patch Manager excels in automating the patching process, especially for Microsoft products, providing significant time savings and enhanced security.
SolarWinds expands on WSUS and helps to decrease the risks to your organization’s security by providing your systems with the latest security patches from Microsoft. Where Solarwinds Patch Management differs from WSUS is that the installation of patches and updates are scheduled before being implemented, giving organizations much less downtime.
SolarWinds Patch Manager still lets you use SCCM, so you can keep all of your equipment up to date and secure with the latest patches and updates, for 3rd-party applications as well. There is also a great reporting tool that helps to show patching compliance and summary reports, while still remaining compatible with WSUS patch management.
SolarWinds Patch Management offers the best of both worlds as it keeps both Windows patches up to date, as well as third-party applications, giving your organization all of the updates to security that it needs. It has an integration with SCCM and it can move the updates for third-party software packages into the native Windows patching process. This enables coordination of patching for issues such as patch dependencies and rebooting.
The tool’s dashboard shows the completion status of each patch run, displaying the completion status and a reason code if patches failed to apply. The patches can then be tested individually and scheduled for rerun or excluded from the scheduler in the event of irreconcilable problems. The SolarWinds Patch Manager uses the WSUS update agent to implement its services. Logging records the actions of the update process and outcomes, which is useful for compliance reporting.
Who is it recommended for?
Best suited for organizations with a strong focus on Microsoft environments and those seeking a comprehensive solution for both Windows and third-party patch management.
Pros:
- Simple dashboard makes it easy to track and visual patches and their progress, even on larger networks
- Integrated directly with SCCM for a smoother patch deployment
- Supports a wide variety of third-party patching options
Cons:
- The tool is very enterprise focused, may not be the best option for home labs or small networks
Download a 30-day free trial.
4. NinjaOne Patch Management – FREE TRIAL
NinjaOne, formerly NinjaRMM, is a cloud platform that provides all of the tools that the technicians of a managed service provider (MSP) need in order to support the system of a client company. The remote system management tools included in the NinjaOne plan would also be suitable for use by an IT department that manages the systems of several remote sites. NinjaOne's consistent ranking on G2 underscores its reliability in RMM, Patch Management, and Endpoint Management.
Key Features:
- Fits with NinjaOne RMM
- Multitenanted for MSPs
- Operates on Windows and macOS
- Third-party software updates
Why do we recommend it?
NinjaOne offers a robust cloud-based patch management system integrated with RMM, suitable for diverse environments and capable of handling a broad range of software packages.
Patch management is one of the important tasks that any system management team needs to perform and an automated patch manager is integrated into the NinjaOne package. This system will track the versions of Windows and macOS running on your endpoints and servers and poll for available patches, queuing them up to be applied. The operating system management functions extend to the updates and replacements for system services and hardware drivers. These system updates can be managed directly in the NinjaOne console or channeled through a WSUS server for rollout.
As well as operating systems, NinjaOne’s patch manager will monitor the statuses of 135 software packages.
In all cases, the patch manager copies over the patch package from its original source and stores it. The available patches are then listed for implementation, giving the operator the option of holding back one patch for investigation while allowing all others in the list to be applied.
Patch rollout can occur on a schedule to be applied overnight and the system is also able to implement reboots after implementation where necessary. The console also allows for patches to be applied immediately, on-demand. Patches can be applied in bulk or individually.
Who is it recommended for?
Recommended for MSPs and IT departments managing Windows and macOS environments who need an efficient, scalable patch management solution.
Pros:
- Can silently install and uninstall applications and patches while the user works
- Patch management and other automated maintenance tasks can be easily scheduled
- Platform agnostic web-based management
Cons:
- Lacks support for mobile devices
The NinjaOne system is a subscription service with a rate per monitored device. Contact the NinjaOne sales team for a quote. NinjaOne is a cloud platform and so is accessed through a browser; you don’t need to download it. You can access the system on a 14-day free trial.
5. SuperOps Patch Management – FREE TRIAL
SuperOps.ai is a SaaS platform that provides services for managed service providers. The system includes a remote monitoring and management system, called SuperOps RMM and a professional services automation package, called SuperOps PSA. SuperOps RMM includes a Patch Management module.
Key Features:
- Part of an RMM
- Suitable for MSPs
- Scheduled operations
Why do we recommend it?
SuperOps provides a versatile patch management solution within its RMM platform, focusing on Windows environments and offering customizable scheduling options.
The SuperOps Patch Management service watches over desktops and laptops that run Windows. The RMM package includes three other modules and one of these is an Asset Management service. The asset manager’s routines perform network scans, identifying each endpoint and creating an asset inventory. Each Windows device is then analyzed, producing a software inventory.
The software inventory of SuperOps forms a basis for the work of the Patch Management system. This service checks with all of the producers of the software packages listed in the inventory, looking for updates. It also scans Microsoft’s feeds for new patches for the versions of Windows that are known to be running on the managed site.
When the Patch Management system detects a new patch or update, it copies over the installer, storing it on the SuperOps server. The subscriber needs to set up the Patch Management service to dictate how it should operate. One of these setup tasks is to define a maintenance window calendar. The next is to decide whether new patches should wait to be approved before they are scheduled for rollout or if the Patch Management system should just apply them automatically at the next available maintenance window.
Patch application should occur overnight and so it is unlikely that a technician will be on hand to watch the process. The dashboard shows completion statuses for the patches in a run and also logs all actions that occurred during the rollout.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for MSPs and larger in-house IT teams looking for a hybrid RMM/PSA solution with flexible patch management capabilities.
Pros:
- Highly customizable – great for companies looking to build their own SOPs
- Is a hybrid RMM/PSA solution
- Flexible cloud-based product
- Great option for MSPs and larger in-house teams
Cons:
- Would benefit from a longer 30-day trial
Pricing:
| Solo | PSA + RMM for single, independent technicians: Free for the first year |
| Starter | PSA only: $89 per technician per month |
| Growth | PSA and RMM for small MSPs: $109 per technician per month |
| Premium | PSA and RMM plus a Project Management module: $129 per technician per month |
This is a cloud based package, so there is no download but there is a 14-day free trial,
6. N-able N-sight Patch Manager – FREE TRIAL
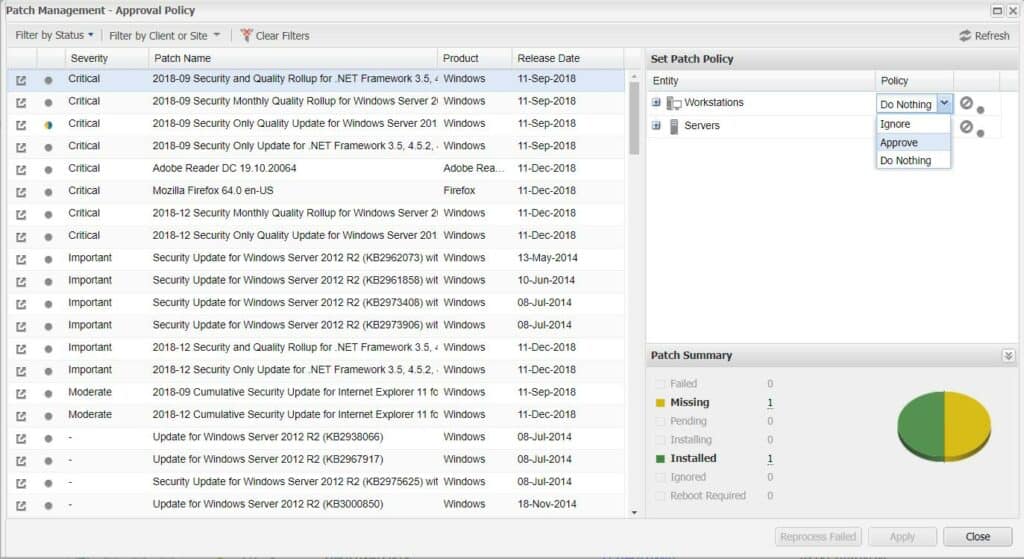
The N-able N-sight Cloud Patch Management software is a hosted service and part of a wider platform of tools for technicians. This is a remote monitoring and management system that is suitable for managed service provides (MSPs) and IT departments with multiple sites to support.
Key Features:
- A service for MSPs
- Cloud-based
- Mainly Microsoft patches
Why do we recommend it?
N-able N-sight offers scalable cloud-based deployment for patch management, particularly strong in Windows environments, with automated discovery and a wide range of administration options.
This tool is particularly suited to patching Windows on endpoints and servers. It is able to identify all devices connected to the network and it keeps the equipment inventory up to date automatically. That discovery service also includes the creation of a software inventory for all devices. This includes the patch status of each operating system instance and all of the software on each device.
The Patch Manager retrieves new patches from suppliers automatically. The main source for these is Microsoft because this is the source for operating system patches and also for software and applications, such as Office and Exchange Server. The N-able N-sight also scans other software providers for updates, such as Oracle for its Java packages and the services provided by Adobe.
Patch rollouts can be automated and scheduled so they occur out of office hours. The technician arriving to work on the morning after a rollout gets a report on the success or failure of each patch. Failed patches can be investigated and then reapplied on demand.
Who is it recommended for?
Suitable for MSPs and IT departments of any size, especially those seeking a comprehensive cloud-based solution for patch management and automated inventory management.
Pros:
- Excellent monitoring dashboard, great for MSPs or any size NOC teams
- Scalable cloud-based deployment
- Monitor for anywhere via web browser
- Automatic asset discovery makes inventory management easy, even on busy networks
- Wide variety of automated remote administration options make it a solid choice for helpdesk support
Cons:
- The platform can take time to fully explore all of its features and configuration options
Get a 30-day free trial of with its Patch Manager.
7. ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus – FREE TRIAL
ManageEngine is no stranger to enterprise product design, and for all of your workstation and server patching requirements they have created Patch Manager Plus.
Key Features:
- Operates on Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Software updates
- Pre-validated patches
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Patch Manager Plus provides a flexible and comprehensive patching platform, supporting multiple operating systems and over 250 third-party applications.
This is a comprehensive, all round patching platform that offers automated patch and patch deployment for multiple operating systems such as Windows, MacOS, Linux, as well as over 250 third party applications.
Best of all, you have the option of going traditional with an on premise installation, or implementing a cloud version of it, the choice is yours, based on the operational requirements of your business.
Patch Manager Plus is able to scan endpoints and detect any missing patches that your computer might have, allowing you to keep your systems updated and patched to protect you and your organization from malicious threats on the internet.
Even better, Patch Management Plus is able to test and deploy patches before you have even installed it yourself, so that it can detect and mitigate and system security issues.
Deployment is easy, simply setup and schedule it and it will automatically update and deployed whenever you want it to. Even better are the reports that can be generated on the network, which gives you all of the information that you need to ensure that you are running a tight ship.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for enterprises or MSPs seeking a versatile patch management solution with extensive cross-platform support and in-depth reporting capabilities.
Pros:
- Flexible deployment options across multiple platforms
- Can be installed on both Windows and Linux platforms, making it more flexible than other on premise options
- Offers in depth reporting, ideal for enterprise management or MSPs
- Integrated into more applications than most patch management solutions
Cons:
- MangeEngine is a feature rich platform that takes time to fully explore and learn
There are two different versions: Professional and Enterprise. There are quite a few differences between the two product types, so be aware of these when looking at which one is best for you.
Start with a 30-day free trial.
8. SecPod SanerNow Patch Management – FREE TRIAL
SecPod SanerNow Patch Management offers system security tools and asset management services in a SaaS package. All of the processing of data for this system is performed on the cloud, so you don’t have to host the system on your own servers or maintain its software.
Key Features:
- Patches Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Software updates
- Scans for misconfigurations
Why do we recommend it?
SecPod SanerNow offers a hybrid security and patch management solution, excelling in cross-platform support and automated asset tracking, making it a strong choice for larger environments.
The SecPod SanerNow cyber-hygiene system includes a lot of security management automation. This starts with a vulnerability manager. The vulnerability scanner runs periodically on your network. It is able to reach endpoints running Windows, macOS, and Linux. The service checks all of the ports and also looks at the configuration of the device. It then moves up from settings to check the operating system version and up to the software installed on the device, looking at how they are set up and what versions they have.
This vulnerability sweep interacts with the asset manager in the package. It updates information about the operating systems and software running on each device. The vulnerability manager then passes over to the patch manager. This checks through the asset manager’s software inventory and then polls the suppliers of those products for patches and updates. If any are available, it copies over the installers and lists them in the console of SanerNow.
The SecPod SanerNow dashboard is hosted on the SecPod servers and can be accessed from anywhere through any standard Web browser. The patch manager screen in this console shows a list of pending patches. You set up the system to give it specific times of the day and days of the week when it can run safely. So, the patch manager will roll out all current pending patches at the next available window.
Who is it recommended for?
Recommended for organizations seeking a cloud-based patch management solution with additional security and IT asset management capabilities.
Pros:
- Offers ITAM capabilities through a SaaS product, making it easier to deploy than on-premise solutions
- Features cross-platform support for Windows, Mac, and Linux
- Can automate asset tracking, great for MSPs who bill by the device
- Can scan for vulnerabilities, make it a hybrid security solution
Cons:
- Better suited for larger environments
The patch rollout will happen unattended. Systems administrators can see the termination status of each patch application. If there are problems, the remaining patches can be launched manually.
SecPod SanerNow Patch management is charged by subscription the sales team negotiates the price with each client. There is no download for this cloud-based service. Instead, you should access a 30-day free trial.
9. Heimdal Security – FREE TRIAL
Heimdal Security enables efficient Windows system and application patching, acting as a WSUS replacement if desired.
Key Features:
- Combined security and vulnerability management
- Asset management capabilities
- Support for 120+ applications
- Windows patch management automation
Why do we recommend it?
Heimdal Security provides efficient Windows and Linux patching with an intuitive dashboard, offering fast P2P patch distribution and comprehensive auditing capabilities.
Heimdal Security offers patch management for Windows and Linux-running machines. It can install, deploy, and push updates & patches on any system regardless of build or network environment.
Heimdal Security deploys new 3rd party patches silently to your endpoints, based on configured policies. No manual input, reboots, or interruptions needed. You can also use the Infinity Management add-on to deploy and patch custom applications that support silent installation commands.
Who is it recommended for?
Best for system administrators needing a scalable and user-friendly patch management system, particularly for Windows and Linux environments.
Pros:
- Fast P2P patch distribution
- Highly intuitive patch management dashboard
- Ability to audit and report on patching processes
- Highly scalable
Cons:
- Can take time to explore all options and features fully
The platform’s intuitive interface makes it easy for any system administrator to craft a custom patch management policy for their network or multi-tenant clients.
Start with a 30-day free trial.
10. Microsoft SCCM Patch Management
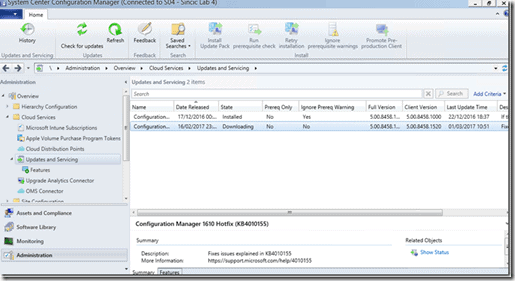
SCCM (System Center Configuration Manager) is Microsoft’s enterprise solution to keeping all servers and workstations patched and updated with the latest security updates, and a whole lot more. It works with a whole selection of different operating systems, and not just the Microsoft eco-system.
Key Features:
- OS deployment
- Patching for Windows
- Microsoft software updates
Why do we recommend it?
Microsoft SCCM is a comprehensive solution for patch management, software updates, and OS deployment, particularly effective in Windows-centric environments.
It allows for system administrators to perform tasks remotely, reducing the time needed to diagnose, update and troubleshoot systems throughout the organization. It is therefore able to offer patch management, software updates and even OS deployment all from a single application.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for system administrators in organizations heavily reliant on Microsoft products, seeking a full suite of patch management tools.
Pros:
- Is a full suite of patch management tools
- Can manage patches for a variety of Windows tools
- Ideal for system administrators
Cons:
- Better suited for Windows products
Pricing varies from site to site, depending on what added features you require, such as endpoint protection, so pricing will be different depending on your business needs.
11. Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Manager
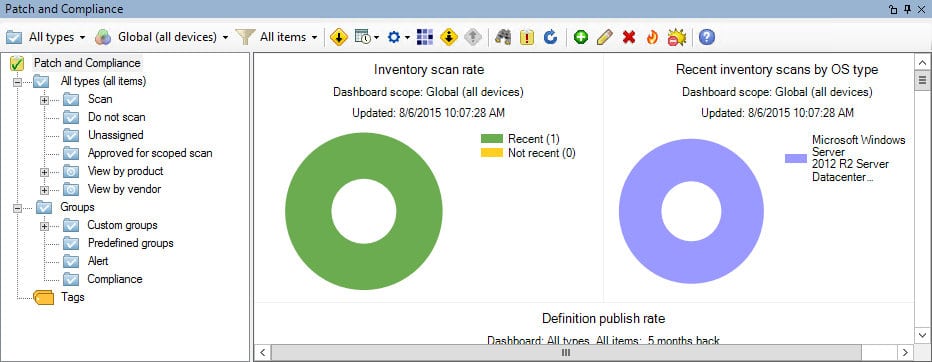
Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Manager provides vulnerability scanning and patching for computers running Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Ivanti gathers all patches for operating systems and software packages as they become available – the company tracks the major software systems.
Key Features:
- Operates on Windows, macOS, and Linux
- A library of pre-assessed patches
- Scheduled rollout
Why do we recommend it?
Ivanti Patch for Endpoint Manager provides thorough patching for multiple platforms, complemented by a vulnerability scanner, making it a comprehensive choice for endpoint security.
When a patch becomes available, Ivanti evaluates it and then stores approved updates in its library. Each instance of Patch for Endpoint Manager periodically checks this register for any available patches that relate to software installed on the site it protects. If any are available, it copies down the installed and schedules it for rollout.
This patch manager offers a little more than system updates because it incorporates a vulnerability scanner. Any discovered vulnerabilities that relate to software versions will be passed over to the patch manager but misconfigurations will be listed for the system administrator to deal with.
Patching can be held off and implemented on a regular day of the week, such as Patch Tuesday. In an emergency, the administrator can launch the patch batch manually, or pick one patch in the list for immediate implementation.
Who is it recommended for?
Recommended for IT teams seeking a patch management solution with added vulnerability scanning capabilities, suitable for Windows, macOS, and Linux environments.
Pros:
- Automated and manual patch launch
- Scheduled for unattended execution
- Completion status reports
- Logging for compliance reporting
Cons:
- No price list
Download: Get access to a free trial.
12. Kaseya VSA Patch Management
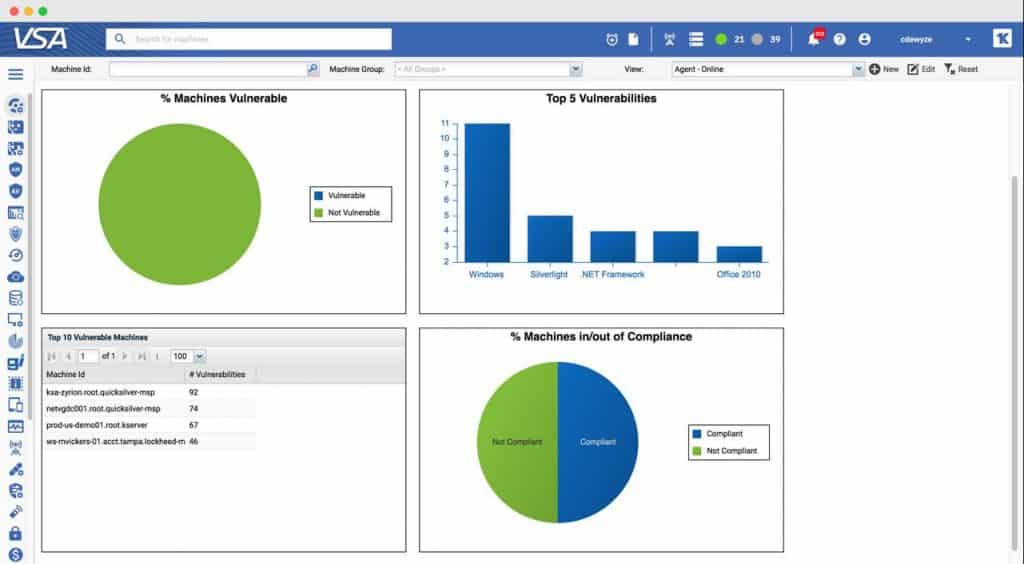
Kaseya VSA Patch Management is slightly different from most of the other products that we have already looked at today, mainly because of the added functionality that it brings with it. It not only allows you to patch Microsoft Windows machines, but Mac and third-party applications as well. This means that you can rest assured knowing that all of your systems on the network will be up to date and secure, regardless of whether they are Windows or Mac based.
Key Features:
- Part of an RMM
- Good for MSPs
- Windows and macOS
Why do we recommend it?
Kaseya VSA offers a versatile patch management solution suitable for MSPs, with capabilities extending to Windows, macOS, and third-party applications.
Once you have installed the VSA Patch Management Module, you will be able to patch, monitor and deploy software from a single platform.
All of your software updates and patches occur from within this single console, giving you and your team all of the control that they need to keep your environment secure and up to date.
Where Kaseya really starts to shine is in the visibility front. It is able to give your team a really good picture of what is updated on your system and is healthy, while highlighting compromised and outdated systems that need to be upgraded.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for MSPs and IT teams needing a comprehensive patch management system with a focus on both Windows and macOS environments.
Pros:
- Automated software deployments can help streamline adding new machines to the client network
- Does a good job at monitoring overall health and resource consumption of devices
- Interface is simple and customizable
Cons:
- Free trial could be longer
13. GFI LanGuard
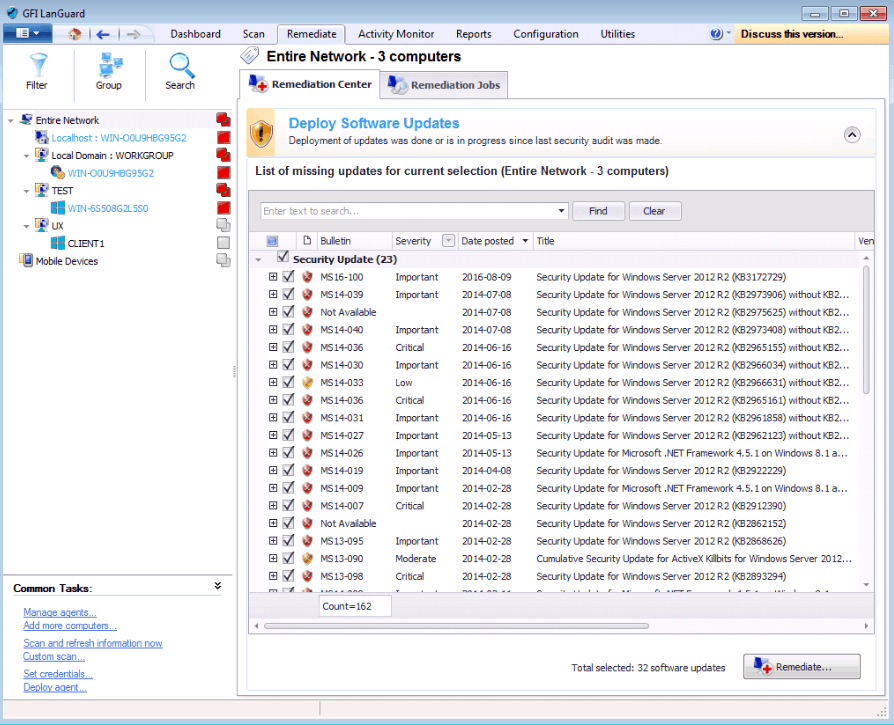
GFI LanGuard has a patch management feature that allows it to fully scan your network, and automatically find vulnerabilities and apply patches. This can be configured to run as an automated service, or as a user driven, on demand service.
Key Features:
- Windows, macOS, and Linux
- Vulnerability scanner
- Patch rollback
Why do we recommend it?
GFI LanGuard excels in network-wide patch management with a focus on security, offering multi-platform support and the ability to roll back patches if needed.
Whichever configuration you decide on you can count on the system to find all of the outdated software on your network. This includes both security related patches and non-security related patches. If you accidentally apply a patch without first testing it, and it causes issues on your network, there is a roll back feature.
The rollback feature takes away the last patch, or patches that are suspected to be causing issues on the network. GFI LanGuard offers Microsoft Windows, Mac OSX and Linux support, as well as the third-party applications that accompany them.
Who is it recommended for?
Best suited for organizations looking for a robust patch management tool with strong vulnerability assessment features and multi-platform support.
Pros:
- Multi-platform support for Microsoft, Linux, and Mac
- Includes support for patching other popular third-party applications like Adobe, Java, and Runtime
- Simple, yet effective interface
- Built-in vulnerabilities assessment uses patch information to help gauge risk for security teams
Cons:
- Would like to see more features for scheduling patches
- Could use more up to date support for newer third party applications
14. ITarian Patch Management
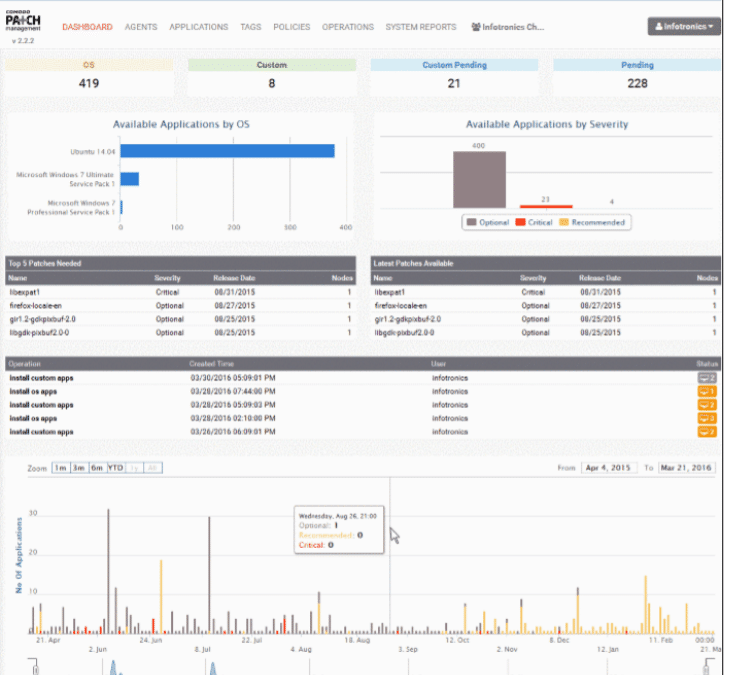
ITarian Patch Management (formerly Comodo Patch Manager) is a patch management module that is aimed at system administrators. It has been designed to give admins granular control over the environment that they oversee, and allows for fine tuning and customization of the patching and updating process through its console.
Key Features:
- Part of Comodo product family
- Windows, macOS, and Linux
- OS deployment
Why do we recommend it?
ITarian Patch Management provides comprehensive patching capabilities with a focus on user-friendliness and automation, suitable for diverse IT environments.
It allows for deployments and updates of not only operating systems but third-party applications as well. It is able to do this thanks to the centralized design of the system, as well as the user-friendly, easy-to-use interface.
It can therefore do almost anything to do with updating and patching, such as deploying operating systems remotely over the network for Windows, Linux and Mac, as well as the third party applications that are often found installed on them.
This helps endpoint identification, and lets the users know which systems need to be patched and updated. This saves your IT staff time and money in the long run, making it really convenient.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for system administrators seeking granular control over patching processes, with support for Windows, macOS, and Linux platforms.
Pros:
- Simple interface is easy to learn on your own
- Can automatically discover machines on the network
- Patching policies are easy to create
Cons:
- Can support Linux in a limited capacity, but was built more for Windows
15. Symantec Patch Management Solution
Symantec are best known for their antivirus products that were once among the most popular in the world, but they now have a patching solution as well. This allows your IT staff to proactively manage the patch software on your network, without you having to wait for something to break before you can act.
Key Features:
- Operates on Windows
- Detect each computer’s patch status
- Activity logging
Why do we recommend it?
Symantec's patch management solution offers a user-friendly interface and efficient patching features, making it a solid choice for proactive patch management.
The process of updating your software is automated, meaning that you no longer even have to initiate the updates, but instead you can schedule everything to download automatically.
Who is it recommended for?
Recommended for organizations seeking an easy-to-use patch management tool with strong features for Windows environments.
Pros:
- Balances usability with in-depth patching features well
- Uses helpful wizards during the patch setup process
- Uses a simple interface for fast patch monitoring
Cons:
- Pricing is not transparent, must contact sales
Symantec have released a highly detailed data sheet which can be downloaded from here.
Related Post: Windows Monitoring Software and Tools
Conclusion
Keeping your infrastructure up to date is critical if you are going to enjoy hassle-free computing within your company. There are important reasons why patching is necessary, but the most important is to keep your company’s information safe, while not letting hackers and cyber criminals into your network.
Patching solutions can automate this process to a large extent, even letting your applications update to the latest, more secure versions. There are so many different solutions out there that it is impossible to recommend only a single one.
Many of the examples that we have shown you today have free versions that can be used on a trial basis, and can be purchased afterwards if you find the application useful. We hope that you have found all of this information useful, and that you can now make an informed purchase!
Patch Management FAQs
What is patch management?
Patch management is the process of identifying, deploying, and managing software patches to fix security vulnerabilities or other issues in computer systems and applications.
Why is patch management important?
Patch management is important because it helps prevent security breaches and other issues caused by software vulnerabilities. By ensuring that software is up-to-date and patched with the latest security fixes, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access, data loss, and other security incidents.
What types of software are typically included in patch management?
Software that is typically included in patch management includes operating systems, web browsers, productivity software, and other commonly used applications.
What are some common patch management tools?
Common patch management tools include commercial solutions like Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager, IBM BigFix, and Ivanti Patch Management, as well as open-source solutions like WSUS (Windows Server Update Services), WPKG, and Opsi.
What are some best practices for patch management?
Some best practices for patch management include implementing a patch management policy that outlines the process and criteria for patch deployment, prioritizing patches based on the level of risk they pose, using automated patch management tools to reduce the risk of human error, testing patches in a non-production environment before deployment, and regularly reviewing and updating patch management policies and procedures.
What are some potential risks or drawbacks of patch management?
One potential risk of patch management is the potential for patches to cause unintended consequences, such as system crashes or compatibility issues with other software. This is why testing and evaluation before deployment are critical. Another potential risk is the possibility of a patch not being deployed quickly enough, leaving the system vulnerable to attack. It's important to balance the need for patching with the risk of disruption to system availability and performance.