Nagios, one of our all time favorite network monitoring tools for Linux, can sometimes be a little overwhelming when setting up, maintaining and keeping up to date. All configurations are done through config files and can be cumbersome and quite frankly, inconvenient. Many admins and engineers who are not familiar with Linux/Unix commands and architecture prefer to work within Windows Server/Desktop instead, with a more Fully Automated approach.
- Paessler PRTG – FREE TRIAL Offers a free version for up to 100 nodes and comprehensive infrastructure monitoring.
- ManageEngine OpManager – FREE TRIAL Monitors up to 1,000,000 interfaces or 50,000 devices with advanced visualization features.
- Site24x7 – FREE TRIAL An all-in-one monitoring platform that provides unified visibility across networks, servers, applications, and user experience.
- SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor Includes a script importer, AI monitoring, and monitoring templates for apps.
- Zabbix A scalable open-source tool operating with minimal overhead, ideal for resource-efficient monitoring.
- OP5 Closely related to Nagios, OP5 offers an easier, more streamlined monitoring solution.
- Zenoss Core Provides both free and paid versions for extensive device monitoring and cloud integration.
- OpenNMS Offers two versions, Horizon and Meridian, with comprehensive network monitoring capabilities.
- Munin A less popular but effective open-source solution focusing on day-to-day resource changes.
On top of the Operating system constraints, there are a ton of plug-ins and add-ons that add to the headache of keeping Nagios up-to-date and functioning properly in a dynamic environment with the wave of BYOD in the workforce.
Some features we're looking for in a replacement are:
- Easy and Fully Automated Network Discovery and SNMP Scanning functionality (without the need for Add-ons or Plugins)
- Commercial, Enterprise and Open-Source Alternatives (for those looking for Freeware alternatives)
- GUI Based Web Interface and Configuration for Windows OS
- Built-in Network Analyzer for Netflow and other flow protocols, including sFlow, IPfix, etc
- Network Map and Topology
- Alerts, Notifications, and Triggers with Email, SMS, and other communication channels
Here's a list of Nagios Alternatives/Replacements of 2025
We'll first start off with a list of Commercial alternatives for those looking for a commercially supported software solution, as some are looking for 24/7/365 Support and Troubleshooting.
Most of these have a Free Trial period (30-60 Days) or Freeware version where you are only allowed a certain number of Nodes or Sensors.
Our methodology for selecting the best Nagios alternative tool:
We've broken down our analysis for you based on these key criteria:
- Compatibility with Nagios for seamless migration, including script importers.
- Extensive support for various applications and pre-built monitoring templates.
- Scalability to monitor a vast array of nodes, sensors, and systems.
- Intuitive and customizable dashboards for effective troubleshooting and problem-solving.
- Comprehensive monitoring capabilities, including agent-less, agent-based, network mapping, and discovery.
1. Paessler PRTG – FREE TRIAL
Paessler PRTG is another great alternative to Nagios, in terms of a commercial replacement. They even have a Free Version that allows you to monitor up to 100 Nodes at No additional cost. Anything over those initial 100 nodes of monitoring will incur licensing fee's but their prices seem to be on par with the rest of the commercial offerings here.
Key Features:
- Free version for 100 nodes
- Comprehensive infrastructure oversight
- Intuitive network maps
Unique Feature
It provides in-depth information about every device like routers, switches, etc. It can also provide metrics for hardware like fan speed, temperature, etc. All these aspects make PRTG an invaluable tool for all environments.
Why do we recommend it?
Paessler PRTG is recommended for its versatility and user-friendly interface, making it an excellent choice for businesses looking for detailed oversight of their infrastructure with minimal learning curve.
PRTG is known for its high-level overview of your infrastructure and monitors it in a way that gives you complete control and oversight into all systems, IP Interfaces, bandwidth and bottlenecks on your network. With their intuitive network maps, alerting and trigger systems, and automatic network discovery, this makes for a great replacement.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is suitable for a range of users, from small businesses utilizing the free version to larger enterprises needing detailed network monitoring and custom reporting.
Pros:
- Drag and drop editor makes it easy to build custom views and reports
- Supports a wide range of alert mediums such as SMS, email, and third-party integrations into platforms like Slack
- Supports a freeware version
Cons:
- Is a very comprehensive platform with many features and moving parts that require time to learn
Pricing: You can start with a 30-day free trial.
Download: https://www.paessler.com/download/prtg-download
Related post: We've compared PRTG vs Nagios here.
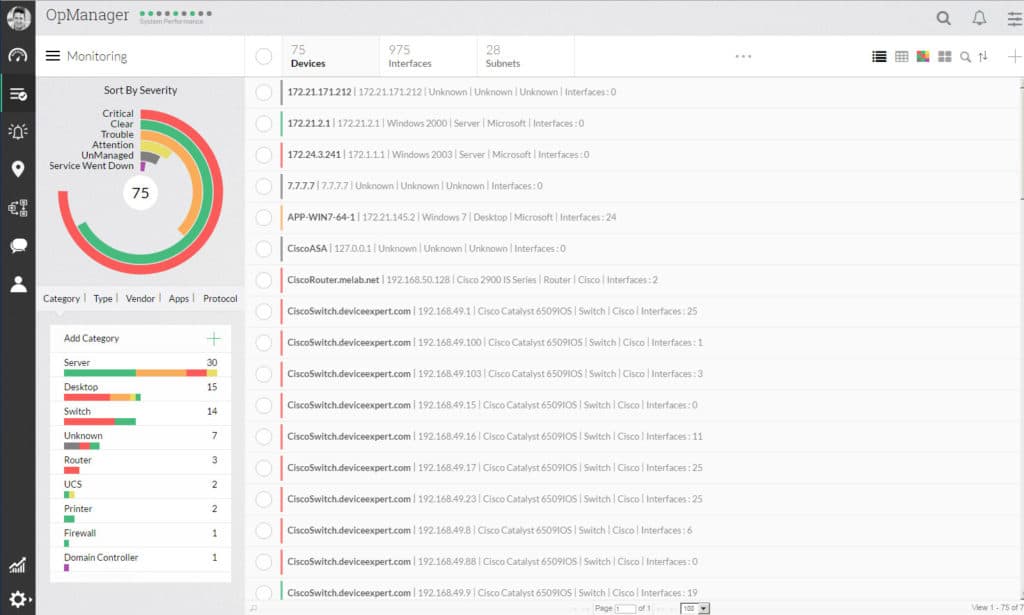
2. ManageEngine OpManager – FREE TRIAL
ManageEngine is consistently redefining the way we look at network management and monitoring, with their OpManager offering which has a full array of features that really make this a great all-in-one tool for any Network Engineer.
Key Features:
- Monitors 1,000,000 interfaces
- 3D DataCenter visualization
- Integrates with ManageEngine products
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine OpManager is recommended for its extensive monitoring capacity and visualization tools, which are particularly useful for large-scale network and data center management.
Some features that stuck out to us was monitoring up to 1,000,000 interfaces or 50,000 devices from a single server, as well as 3D DataCenter layout and configuration for Visualisation. This includes Network Topology Maps, Auto-discovery, WiFi monitoring, heat maps and other functions.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is best suited for medium to large-sized enterprises that require detailed and extensive network monitoring, especially those with complex network topologies and data centers.
Pros:
- Can monitor bandwidth consumption as well as alert to configuration changes that could impact network performance
- Can monitor bandwidth and resource consumption on the application level, and even drill down to identify specific users consuming the most resources
- Supports email, SMS, and webhook for numerous alerting channels
- Integrates well in the ManageEngine ecosystem with their other products
Cons:
- Takes time to full explore the all the options available in the ManageEngine software suite
Price: Work out your network requirements with a 30-day free trial.
Download: https://www.manageengine.com/network-monitoring/
3. Site24x7 – FREE TRIAL
Site24x7 is a powerful cloud-native observability platform. It is one of the most compelling alternatives to Nagios XI—especially for teams who want full-stack visibility without the burden of having to manage on-prem infrastructure. Built by ManageEngine (Zoho Corp.), Site24x7 offers a plug-and-play monitoring solution that unifies network, server, application, log, and user experience monitoring under a single SaaS roof. Unlike Nagios, Site24x7 requires no local installation. Its cloud-first architecture enables faster onboarding and automation across modern stacks, including Kubernetes, AWS, and Azure.
Key Features:
- Unified monitoring for websites, servers, apps, APIs, cloud, and containers
- Native support for AWS, Azure, GCP, Docker, Kubernetes, VMware
- RUM, synthetic checks, and SLA reports included
Unique Feature
Offers a Nagios migration incentive: send proof of your current Nagios XI license and receive 10% off + free usage until your Nagios license expires—a rare, user-friendly transition offer in the industry.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend Site24x7 for organizations transitioning from legacy tools like Nagios, but still needing enterprise-grade monitoring and uptime visibility. Site24x7’s features, like the browser-based setup and cloud-native scalability, make it far more agile for hybrid or distributed environments. We recommend this tool because you can save time with its automatic discovery and preconfigured templates. And the best part is that you don't need to be continuously adjusting config files.
Unlike Nagios, which often requires add-ons and plugins to stay current, Site24x7 comes ready out of the box for multi-cloud monitoring. It also comes ready for application performance management and advanced log analysis.
Who is it recommended for?
Site24x7 is ideal for IT teams and MSPs looking for a unified, low-maintenance observability suite. It is also great for DevOps and SREs seeking real-time monitoring and a modern upgrade from legacy tools like Nagios.
Pros:
- Unified SaaS-native monitoring for cloud and hybrid environments
- Built-in support for RUM, NetFlow, Kubernetes, and container visibility
- No local infrastructure needed
- Competitive pricing with clear TCO advantages
- 30-day free trial and migration perks
Cons:
- Some advanced features (AI alerts, longer log retention) require higher plans
- Slight learning curve for new users unfamiliar with observability tools
Pricing: Start your 30-day free trial (no credit card required).
4. SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor
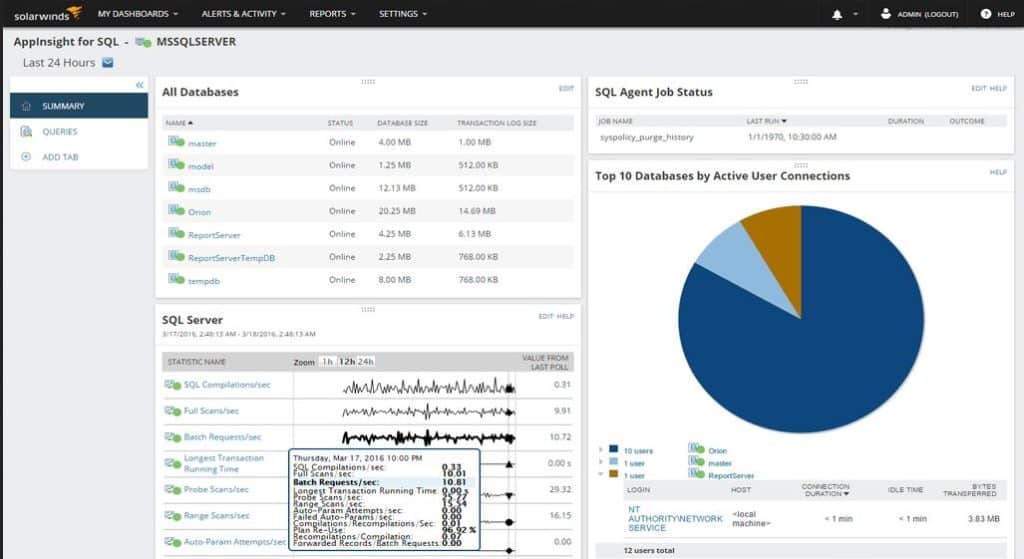
SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor is one of the Most well-supported monitoring solutions around, specifically when it comes to Migrating from Nagios. SolarWinds has a built-in Nagios script importer that allows your to use your existing Nagios scripts that you've developed over the years and directly import them into SAM.
Key Features:
- Nagios script importer included
- Supports over 200 applications
- Scales to thousands of nodes
- Advanced AppInsight dashboard
Unique Feature
This tool sends smart alerts to help you stay on top of issues. Its extensive and well-designed reports help with decision-making, internal auditing, and compliance.
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Server & Application Monitor is highly recommended for its seamless Nagios integration, making it an excellent choice for organizations transitioning from Nagios. Its capability to support a vast number of applications and nodes makes it a versatile and scalable solution for large networks.
For many, the feeling of losing all your work and customization within Nagios is now saved due to this awesome feature. We've seen very few monitoring solutions offer such streamlined support for migration from Nagios into their own platform.
SAM boasts support for over 200 and more applications that are directly built into the software that will allow you to get setup within hours, instead of days or weeks. Their extensive community of IT pro's and engineers have also developed additional templates and support for custom solutions as well. SAM scales up to any number of Nodes and sensors and allows you to monitor thousands upon thousands of systems, services, resources, hardware, and anything else you may want to keep track of.
Their AppInsight dashboard helps you visualize and pinpoint issues quickly and efficiently to help you determine the root cause of the problem or issue. SAM supports agent-less and agent-based monitoring, as well as an intuitive network mapping and discovery feature for quickly mapping out your topology quickly and automatically.
The feature set goes far and beyond what Nagios has to offer, we really suggest downloading a Free Trial and configuring it quickly in your environment. With their 200+ built-in monitoring templates, you'll be up in a couple hours.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for large enterprises and networks that require extensive monitoring and have existing investments in Nagios scripts, seeking to migrate without losing their custom configurations.
Pros:
- Designed with large and enterprise networks in mind
- Has some of the best alerting features that balance effectiveness with ease of use
- Supports both SNMP monitoring as well as packet analysis, giving you more control over monitoring than similar tools
- Uses drag and drop widgets to customize the look and feel of the dashboard
- Robust reporting system with pre-configured compliance templates
Cons:
- This is a feature-rich enterprise tool, small networks may find it overwhelming
Price: To figure out your network requirements and pricing, start of with a 30-day free trial.
Open-Source Replacements
Next, we'll go over some alternatives that are Open-Source and have smaller support communities, but also perform as well as the others listed above.
More often than not, many of the below open-source solutions require greater knowledge and know-how when initially configuring and setting up the software.
On top of that, many of the software solutions below might also need 3rd party plugins or Add-ons to complete certain tasks or perform monitoring on certain brands or manufacturers of hardware, as well as other basic functions that we've mentioned in the list above.
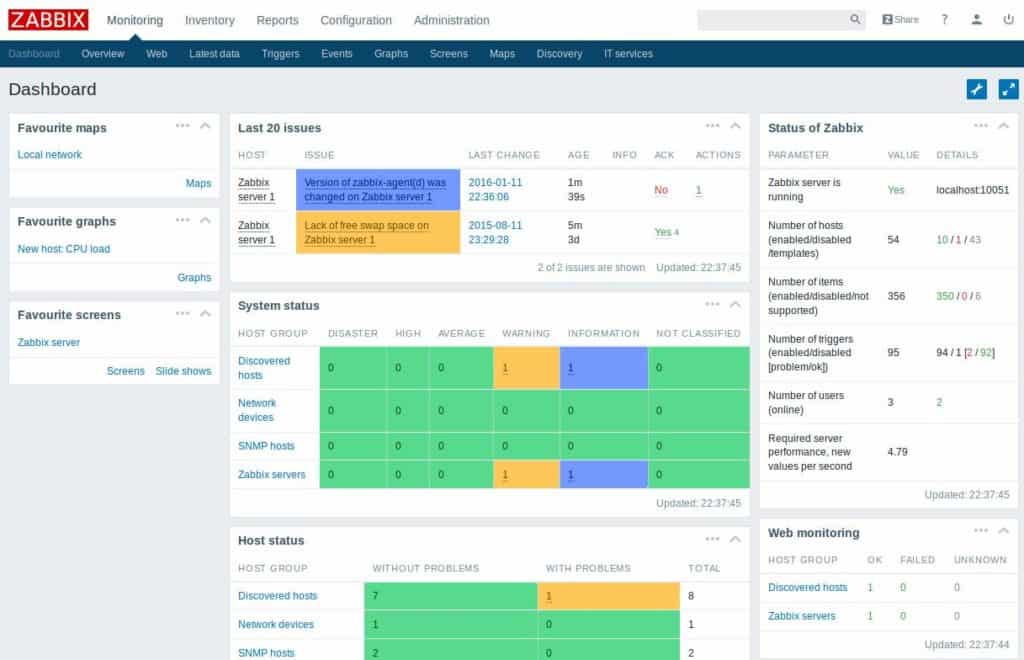
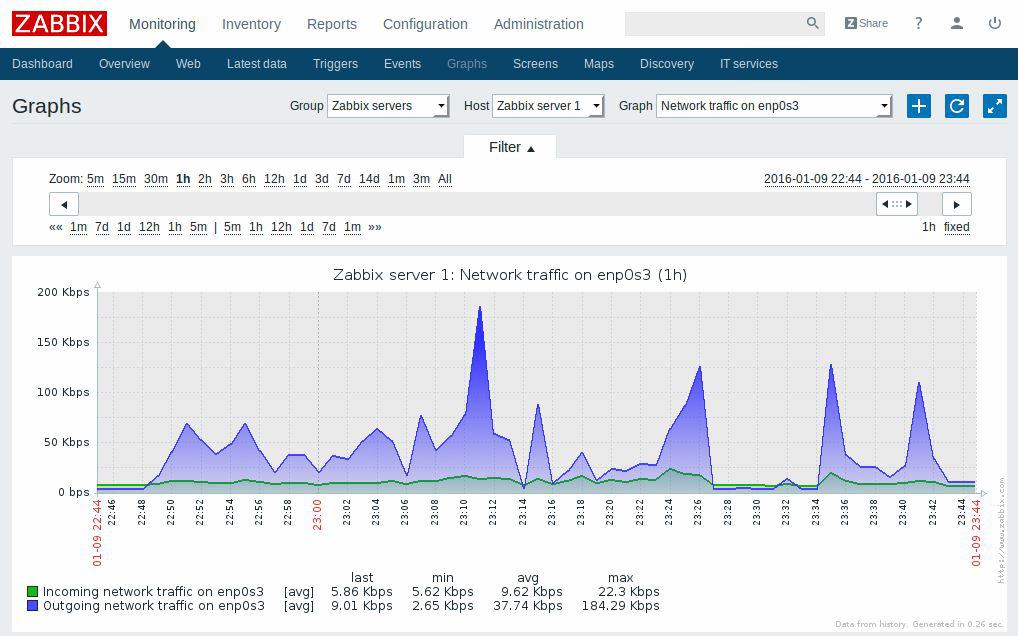
5. Zabbix
Zabbix is one of the top open-source competitors to Nagios due to its scalable design and light overhead, claiming that it can operate with just 256MB of Ram. Fine tuning Zabbix is a little cumbersome, as many have stated, but once your've figured out all the quirks and details, you'll be chugging along nicely.
Key Features:
- Lightweight, scalable design
- SNMP and ICMP monitoring
- Open-source tool
Why do we recommend it?
Zabbix is recommended for its efficient and scalable monitoring capabilities, especially suitable for organizations looking for a cost-effective, open-source solution.
Once again, Zabbix, like most Open-source network monitoring software, can monitor Windows based machines with agents, but will not run on them as a central server. Zabbix can be installed on the following operating systems:
- Linux
- IBM AIX
- FreeBSD
- NetBSD
- OpenBSD
- HP-UX
- Mac OS X
- Solaris
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for businesses of all sizes that prefer open-source solutions and have the technical know-how to set up and customize their monitoring systems.
Pros:
- Open-source transparent tool
- Uses both SNMP and ICMP for broader monitoring ranges
- Offers useful templates for quick insights
Cons:
- No paid support option – not ideal for large enterprise environments
Download information: http://www.zabbix.com/download
6. OP5
OP5 has close relations to Nagios and their development team, in specifically, 2 of their developers were on the Nagios development teams. Having a close relationship to Nagios has helped them developed OP5 into a easier and more streamlined program than Nagios is.
Key Features:
- Streamlined node addition
- Geolocation mapping
- Undo functionality
Why do we recommend it?
OP5 is recommended for its user-friendly interface and efficient management features, making it a great choice for organizations seeking a more streamlined alternative to Nagios.
As many have seen and dealt with, Nagios is very time-consuming to setup and config (via config files) and many times there is only 1 or 2 admins who are familiar with the change process of monitoring systems and nodes.
Op5 took additional steps to make adding nodes and servers very easy and streamlined to save time when adding new Systems to monitor. All of this is done through their Web Interface and this process has proved time and time again to save Sys Admins and engineers on setup time and configurations.
They've also added a lot of nifty features including “undo” functionality that will allow you to roll-back changes in-case of mis-configuration. OP5 put out a great video on how they stack up against Nagios, its definitely worth a watch if your considering moving over to OP5 from Nagios.
Who is it recommended for?
Best suited for large enterprises that require a robust, scalable monitoring solution with an emphasis on ease of use and efficient system management.
Pros:
- Focuses primarily on offering their services to large enterprises
- All features and interfaces are designed to scale and handle large amounts of data well
- Simple widget customizations can be added or removed
- Offers geolocation mapping, and dependency mapping to help visualize complicated network services
Cons:
- Must contact sales for accurate pricing information
- The interface could be made more user-friendly with fewer menu options
Download Information: https://www.op5.com/download/
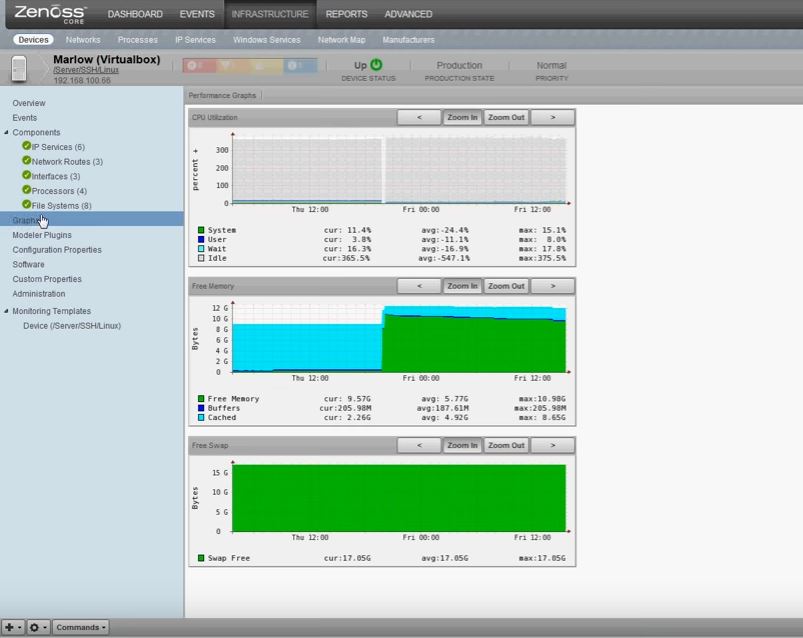
7. Zenoss Core
Zenoss Core offers 3 version of their Open-source solution, including a Free Versions that monitors up to 1000 Devices. As with most of the other software packages here, support for the free version can be obtained through their community forum, which isn't always guaranteed to give you a proper solution or answer to any issues you are dealing with.
Key Features:
- Monitors up to 1000 devices
- Supports cloud resources
- Fortinet monitoring plugin
Why do we recommend it?
Zenoss Core is recommended for its versatility in monitoring both on-premises and cloud resources, making it a comprehensive tool for modern IT environments.
Their 2 paid options, Zaas and Zenoss Service Dynamics, allow you to monitor not only On-premises hardware and software, but Cloud based resources as well. The benefit of using a paid-option of Zenoss Core is the level of service you get from their Support team, along with access to Full Analytics reports and Unlimited Device monitoring. Zenoss Core can install natively on Redhat Linux and CentOS, although Ubuntu and Debian are also options as well.
Who is it recommended for?
Ideal for businesses of various sizes, especially those managing a mix of on-premises and cloud-based infrastructure and looking for a scalable open-source solution.
Pros:
- Offers Fortinet monitoring through a simple plugin
- Uses network discovery to automatically pull in new devices that enter the network
- Supports Cisco Layer 2-4 devices
Cons:
- Support is only for paid tiers
Download Information: https://ownit.zenoss.com/get-started.html
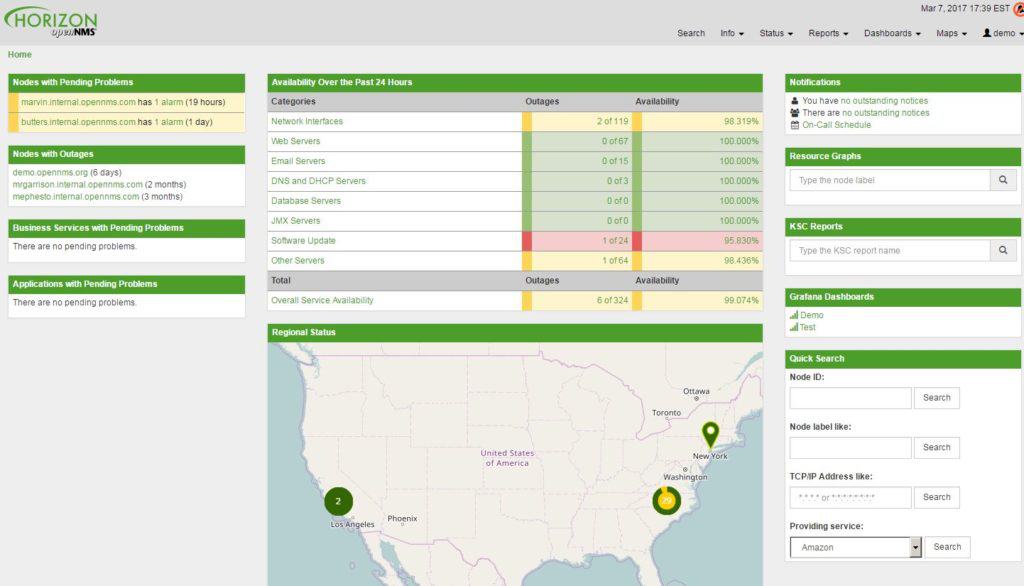
8. OpenNMS
OpenNMS now comes into two distinct versions, or “flavors” as they call it: Horizon and Meridian. Horizon is the free offering that you can download, install and get monitoring without much effort and support, other than their community boards/forums.
Key Features:
- Two distinct versions
- Flexible alert notifications
- Large documentation pool
Why do we recommend it?
OpenNMS is recommended for its flexibility and the extensive support available through its community, making it a solid choice for organizations looking for a customizable open-source monitoring solution.
It is the latest and the greatest with all the updates added to the distribution as they come out. Meridian on the other hand is their Enterprise Grade Subscription service that comes with Pre-Configured reports, layouts, alerts, workflows, and more.
Meridian version has several added benefits compared to the free version, but nevertheless, their community forums and user generated templates really help in setting up the monitoring solution. OpenNMS gives you the option to use either RRDTOOL, JRobin, or NewTS for maximum flexibilty within your environment.
Surprising, OpenNMS has a Windows Server installation, but they do recommend installing and running on LINUX.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is well-suited for organizations that value open-source software and are willing to engage with community forums and documentation for setup and troubleshooting.
Full Feature Set can be found here
Pros:
- Open source projects, lots of room for customization, and personalized add-ons
- Has a large amount of documentation available
- Features two versions, a stable version and a beta test version for new features
- Offers a wide range of monitoring options and flexible alert notifications
Cons:
- Users rely on help documents and forums for support, which isn’t always the quickest way to resolve issues
Download Information: https://www.opennms.org/en/install
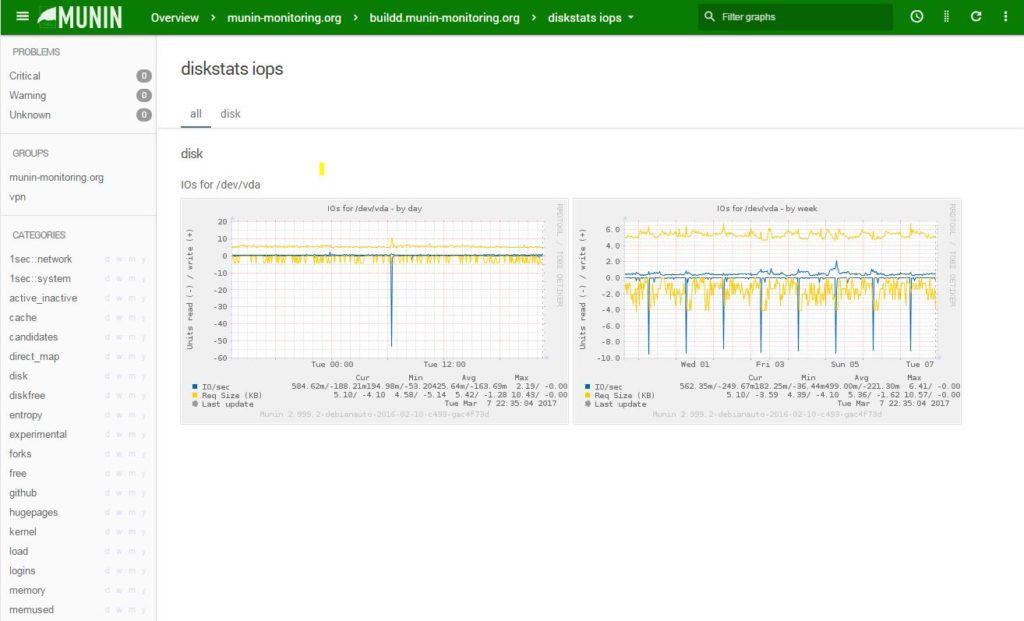
9. Munin
Munin is a not-so-popular monitoring solution, but nonetheless gives you a good replacement if you would like to stick to an open-source solution. Munin is based on Perl and has RRDTOOL integrated into it for graphing functionality.
As many other monitoring solutions function, Munin operates as a master/node configuration and poles nodes continuously for new information and metrics and maps them out as needed using RRD files. Munin has the “what's different today” mindset to ensure that you can see whats different than the prior day and what resources are being used on what machine/system.
Key Features:
- Day-to-day resource tracking
- Lightweight graphical interface
- Master/node configuration
Why do we recommend it?
Munin is recommended for its simplicity and focus on day-to-day changes in resource usage, making it ideal for organizations looking for an easy-to-use, efficient monitoring tool.
Who is it recommended for?
Best suited for smaller organizations or those with Unix and Linux systems, requiring a straightforward, open-source monitoring solution with a focus on resource trends.
Pros:
- Completely free tool
- Easy to use
- Offers live performance graphs
- Uses lightweight graphics that get the job done
Cons:
- Only available on Unix and Linux platforms
Download Info: http://munin-monitoring.org/wiki/WikiStart#download
Nagios Alternatives FAQs
What are some popular Nagios alternatives?
Some popular Nagios alternatives include Zabbix, Icinga, LibreNMS, and PRTG Network Monitor.
Why might organizations look for alternatives to Nagios?
Organizations might look for alternatives to Nagios if they are looking for a more user-friendly or feature-rich monitoring solution, or if they want to reduce the complexity of their monitoring environment.
What are some key features to look for in a Nagios alternative?
Some key features to look for in a Nagios alternative include scalability, ease of use, customization options, and compatibility with a wide range of devices and platforms.
What are some benefits of using a Nagios alternative?
Benefits of using a Nagios alternative can include improved usability, more advanced monitoring capabilities, and reduced maintenance and setup time.
Can Nagios alternatives be used for cloud-based monitoring?
Yes, many Nagios alternatives are compatible with cloud-based infrastructure and can be used for cloud-based monitoring.
What are some common metrics that can be monitored using Nagios alternatives?
Common metrics that can be monitored using Nagios alternatives include network performance, server availability, application performance, and security vulnerabilities.
Related Posts: